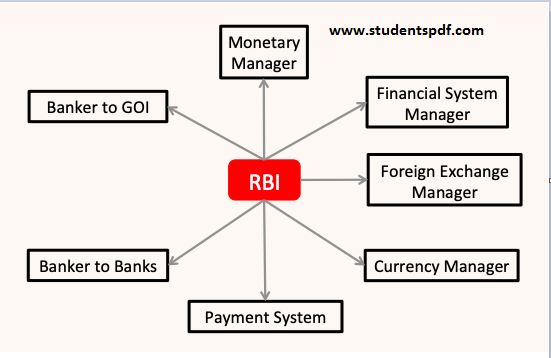
RBI Functions Details, Definitions Of RBI:Reserve Bank of India {RBI} is the Central Bank Of India.RBI was established on 1 April 1935 and nationalised on Jan’1949 passed by an act.RBI plays vital role in the economy,it regulates flow of currency and as well as steady the inflation rate by their monetary policy.Head Quarter Of RBI is in Mumbai.All the major function related to the Policy and regulation of money are under control by RBI.He is the sole issuer of currency in the country,except One Rupee Note which is issued by Ministry of finance.RBI regulates all the bankers in one umbrella.
RBI Functions Details RBI की परिभाषाएँ: भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक {RBI}, सेंट्रल बैंक ऑफ़ इंडिया है। RBI की स्थापना 1 अप्रैल 1935 को हुई थी और यह जनहित अधिनियम के द्वारा पारित जन.1949 को राष्ट्रीयकृत किया गया था। RBI अर्थव्यवस्था में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है, यह मुद्रा के प्रवाह को नियंत्रित करता है और उनकी मौद्रिक नीति द्वारा मुद्रास्फीति की दर स्थिर है। RBI का मुख्यालय मुंबई में है। नीति से संबंधित सभी प्रमुख कार्य और धन का विनियमन RBI के नियंत्रण में है। देश में मुद्रा का एकमात्र जारीकर्ता है, सिवाय एक रुपये का नोट जो वित्त मंत्रालय द्वारा जारी किया जाता है। आरबीआई एक बैंकर में सभी बैंकरों को नियंत्रित करता है।
- {LATEST} LPG POLICY OF 1991 COMPLETE INFORMATION
- Kiran SSC Mathematics 71000+ chapter-wise solved paper Download
Functions of RBI || RBI Functions Details
1.Issues Of Notes:RBI has the Sole right to issue the notes or currency in the country,except one rupee note which is issued by the Ministry of finance.RBI has monopoly to issue the currency notes or coins.RBI has adopted minimum reserve system to regulate or flow the currency in the country.
नोट जारी करना: RBI के पास देश में नोट या मुद्रा जारी करने का एकमात्र अधिकार है, सिवाय एक रुपए के नोट के जो वित्त मंत्रालय द्वारा जारी किया जाता है। मुद्रा नोट या सिक्कों को जारी करने का एकाधिकार है। आरबीआई ने न्यूनतम आरक्षित प्रणाली को अपनाया है। देश में मुद्रा को विनियमित या प्रवाहित करना।
2.Agent or Adviser : RBI an acts as a Agent or adviser to all the banks.He also advise Central govt for making and framing the policy of the Country.He directed and regulated all the banks and commercial banks in a specific manner.He acts as an adviser to the Govt time to time.He also manages the public debts of the government.
एजेंट या सलाहकार: RBI सभी बैंकों के लिए एक एजेंट या सलाहकार के रूप में कार्य करता है। वह केंद्र सरकार को देश की नीति बनाने और तैयार करने की सलाह भी देता है। उसने सभी बैंकों और वाणिज्यिक बैंकों को एक विशिष्ट तरीके से निर्देशित और विनियमित किया है। सरकार के समय के लिए एक सलाहकार। वह सरकार के सार्वजनिक ऋण का प्रबंधन भी करता है।
3.Bankers Bank: RBI has banker of all banks in the country.He performs all the activities which is governed by banks or commercial banks in the country. He acts as a banker to all the bank.Maintained relationship between Central govt banks and state banks in a specific manner.Private Banks or Govt Banks time to time seeks advise from RBI.
बैंकर्स बैंक: RBI के पास देश के सभी बैंकों के बैंकर हैं। वह उन सभी गतिविधियों को करता है जो देश में बैंकों या वाणिज्यिक बैंकों द्वारा संचालित होती हैं। वह सभी बैंक के लिए एक बैंकर के रूप में कार्य करता है। केंद्रीय सरकार के बैंकों और राज्य के बैंकों के बीच एक विशिष्ट तरीके से संबंध रखता है। निजी बैंक या सरकारी बैंक समय-समय पर RBI से सलाह लेते हैं।
4.Credit Controller: The RBI takes responsibility to controlling the credit which is created by commercial bank.RBI takes two major steps to control the credit into the country viz qualitative and quantitative measures.RBI keep watching credit flow so that he takes necessary steps to control the credit.
क्रेडिट नियंत्रक: आरबीआई वाणिज्यिक बैंक द्वारा बनाए गए क्रेडिट को नियंत्रित करने की जिम्मेदारी लेता है। देश में गुणात्मक और मात्रात्मक उपायों में क्रेडिट को नियंत्रित करने के लिए आरबीआई ने दो प्रमुख कदम उठाए हैं। आरबीआई क्रेडिट प्रवाह को देखता रहता है ताकि वह नियंत्रण के लिए आवश्यक कदम उठाए।
5.Foreign Reserves: For the purpose of foreign exchange rate stable,RBI sells foreign currency and alos guard the foreign exchange funds in a specific manner.RBI sells foreign currency in the foreign exchange market ,when supply decrease and vice versa.
विदेशी भंडार: विदेशी मुद्रा की दर स्थिर रहने के उद्देश्य से, RBI विदेशी मुद्रा बेचता है और विशिष्ट तरीके से विदेशी मुद्रा कोष की रक्षा करता है। आपूर्ति कम होने और इसके विपरीत होने पर विदेशी मुद्रा बाजार में विदेशी मुद्रा बेचता है।
6. Miscellaneous Functions: RBI performs some functions to regulate the credit in to the economy.He facilitate credit to NA-BARD to arrange the credit clearing management.
विविध कार्य: RBI अर्थव्यवस्था में ऋण को विनियमित करने के लिए कुछ कार्य करता है। क्रेडिट-क्लियरिंग प्रबंधन की व्यवस्था करने के लिए NA-BARD को क्रेडिट की सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
Conclusion:We can say that RBI is the Central of all the Banks,as an ad visor of the Govt.Performs various functions to control the credit flow in the country. Maintains a healthy relationship between Commercial banks and Private Banks.He is the sole Monopoly to issue the currency and notes.RBI has keep to watchdog control all the measures to ensure the availability of funds in the country.
निष्कर्ष: हम कह सकते हैं कि RBI देश के सभी बैंकों का केंद्र है, जो देश में क्रेडिट प्रवाह को नियंत्रित करने के लिए सरकार के विभिन्न कार्यों के विज्ञापन के रूप में है। वाणिज्यिक बैंकों और निजी बैंकों के बीच एक स्वस्थ संबंध बनाए रखता है। वह मुद्रा और नोट जारी करने का एकमात्र एकाधिकार है। आरबीआई ने देश में धन की उपलब्धता सुनिश्चित करने के लिए सभी उपायों पर नजर रखना है।
Friends, if you need an e-book or notes related to any subject. Or if you want any information about any exam, please comment on it. Like my Facebook page for daily info about our posts.